The similarity between the Turkish and Arabic language

By: Eman El-Ajlouni / Arab America Contributing Writer
It is essential to remember that determining the exact percentage of terms with Arabic origin in Turkish can be difficult since words and terms borrowing and developing can be complicated procedures. However, it is generally agreed that Arabic has had a considerable effect on Turkish lexicon. When the Ottoman Empire was growing and interacting culturally with the Arab world, the Arabic language had a significant historical influence on Turkish. As a result, numerous Arabic terminologies have been translated into Turkish, especially in the fields of law, administration, science, and religion. It is still possible to see this impact in modern Turkish.
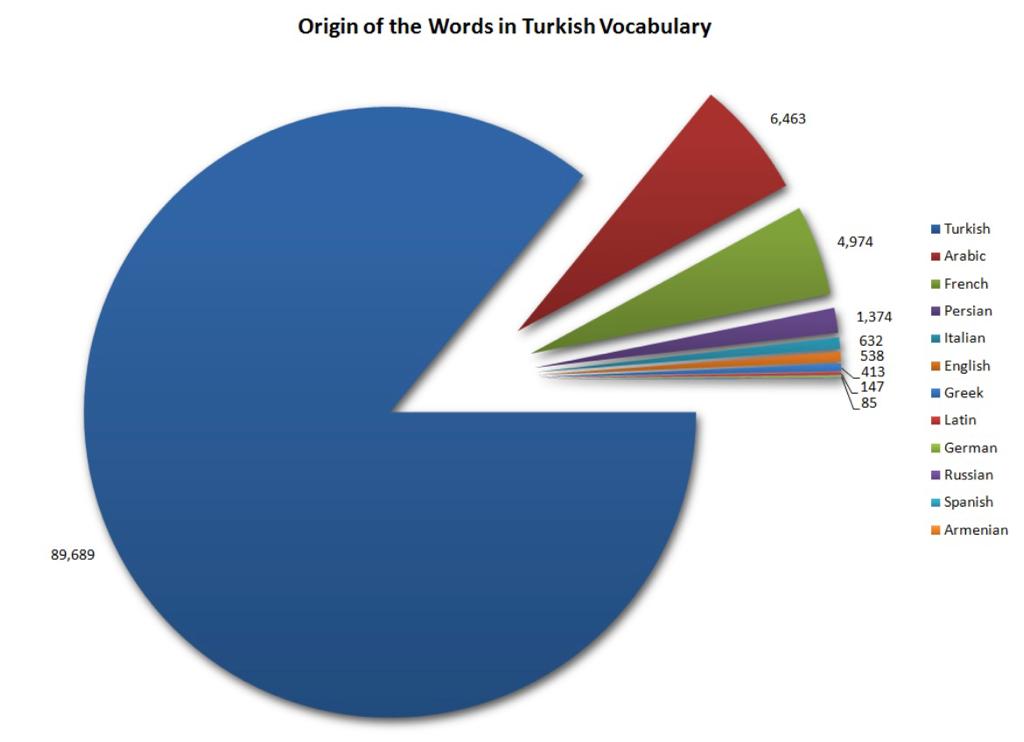
Although it is difficult to give an exact proportion, a study published by the Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism indicates that 6.463 words in the Turkish language have Arabic origins. Due to historical, cultural, and international influences, Turkish has also included vocabulary from other languages, including Persian, French, Italian, and English, among others. The Turkish language now has a vocab that is both rich and diversified as a result of linguistic borrowing and adaptation.
Similarities in the Turkish and Arabic language
It is questioned to what extent Arabic has influenced Turkish culture and how those two cultures interact according to the book “INTERACTION BETWEEN LANGUAGES: THE CASE OF ARABIC AND TURKISH”; Arabic has an impact on Turkish. The majority of Turks practice Islam, and the Arabic translation of Islam’s holy book, The Quran. These are the most significant variables in this context. There are clear Arabic influences in Ottoman Turkish. It is acknowledged that the Letter Revolution of 1928 and the subsequent move for linguistic simplification have led to a progressive decline in the power of Arabic compared to previously. Despite this, Arabic continues to have the greatest influence on Turkish in terms of everyday vocabulary.
Despite being two separate languages from different language families, Turkish and Arabic do have certain similarities, especially as a result of historical and cultural contacts between the places where they are spoken. Turkish and Arabic are comparable in the following ways:
1- Loanwords: Over a period of history, Turkish has taken many words from Arabic, notably in the fields of law, administration, and the sciences. Turkish now possesses a sizable amount of language with Arabic origins as a result of this borrowing.
2- Shared Influence: Other languages have had an impact on both Turkish and Arabic. Turkish has been impacted by a variety of languages, including Persian, French, Italian, and English, whereas Arabic has influenced Turkish through the vocabulary it has borrowed. There are some cross-linguistic commonalities as a result of our shared exposure to different languages.
3- Grammatical characteristics, such as vowel harmony and accumulation, may be found in Turkish and Arabic. Both languages use an affixing system to convey different grammatical functions. In contrast to several other language families, word order in both languages is also rather variable.
4- Historical relationship: Turkish and Arabic are related historically due to Islamic culture and the Ottoman Empire. Cultural and linguistic contact between the two languages has been enhanced by this historical relationship.
Despite these similarities, it’s crucial to remember that Turkish and Arabic have different grammatical structures, phonetic systems, and vocabulary since they are part of separate language families (Turkic and Afro-Asiatic, respectively). Speakers of one language cannot easily grasp the other without prior exposure or study because they are not mutually intelligible.
Similar words in both languages
The Ottoman Empire has held administrative authority over the majority of the Middle East and North Africa since the 16th century, including Iraq, Syria, Palestine, Jordan, Yemen, the Hijaz, Egypt, Tunisia, and Algeria. The Ottomans’ cultural impact continued even after they lost power to European colonial powers in the 19th century
When compared to Arabic, which is a Semitic language and a member of the Afro-Asiatic language family, Turkish is a Turkic language that belongs to the Altaic language family.
The following is a list of several Turkish terms with Arabic origins that are frequently used:
Allah – الله-God
Kitap -كتاب- Book
Merhaba -مرحبًا- Hello
Cami -جامع-Mosque
Sabah -صباح- Morning
Kalem -قلم- Pen
Cennet -الجنة- Paradise
Cehennem -جهنم- Hell
Melek -ملك- Angel
Kur’an -قرآن- Quran
İbadet -عبادة- Worship
Dua -دعاء- Prayer
İmam -إمام- Prayer leader
Hicri -هجري- Hijri (Islamic calendar)
Akıl- عقل- wisdom
Ahlak- اخلاق- ethics
Asker-عسكر- soldier
Basit- بسیط- easy, simple
İnşallah -ان شاء الله- God willing
Conclusion
In conclusion, despite the fact that Arabic has impacted Turkish, the proportion of Arabic-origin words in Turkish is relatively small when compared to the language’s general lexicon, which is predominantly of Turkic origin. Overall, despite the effect of Arabic on Turkish, it still preserves its unique identity as a language with its own grammar, syntax, and lexicon.
Check out Arab America’s blog here!









